Command Line Interface (CLI):-
If you do not Ceragon IP-10 IDU IP address IP detail so you can learn it by Hyper Terminal to login. IDU and other work to set up the IP and login commands -
Click here to download file for commands list
 Microwave Point-to-Point: FibeAirIP-10
Microwave Point-to-Point: FibeAirIP-10
• Manufacturer: Ceragon Networks (Israel)
• Basic parameters:
• Licensed 6-38GHz band (given a choice ODU)
• Bandwidth 7 -56 MHz full duplex (SW tunable)
 • Capacity 10-500Mbps (same HW, license increments)
• Capacity 10-500Mbps (same HW, license increments)
• Interface:
• 1x 1000BaseX (SFP)
• 1x 10/100/1000BaseT
• 5x 10/100 BaseT
• 16x E1
• Integrated Ethernet switch
FibeAirIP-10: The main advantages
• Native TDM (E1) anativníEthernet, with no kind of traffic is mapped over the other, both dynamically share a common bandwidth
• Maximálnívyužití bandwidth
• Low transport delay (<200us 400mbps="" gbe="" nbsp="" p="">• Unique 8-state adaptive modulation for maximum availability, seamless and flawless switching
• Extended support QoS (IPv4/IPv6, Q-in-Q, STP / RSTP / MSTP, ...)
• Statistics (radio, transmission, operation)
• SNMP and HTTP management
• Scalable solution for optimal distribution points (6U)
• CertifikovánoMEF MEF-9-14 (for EPL, EVPL, E-LAN)
• Compact IDU (1U), compact ODU (2.5 kg), low power consumption
• Full scalability (1 +1, 2 +0, Hot standby ...)
• Connect a serial cable to the terminal port
• Setting up HyperTerminal:
• Bit rate: 115200, data bits: 8, parity: none, stop bits: 1 Flow Control: no
• Recommended: type VT-100, size: 24 rows, 80 columns
• Default login:
 • User: admin
• User: admin
• Password: admin
• After pressing get prompt
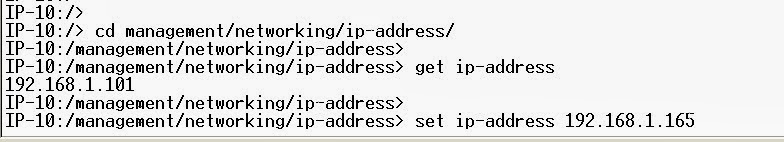
• The IP address IDU:
• IP-10 :/> cdmanagement / networking / ip-address
• IP-10 management :/ / networking / ip-address> get ip-address
If you do not Ceragon IP-10 IDU IP address IP detail so you can learn it by Hyper Terminal to login. IDU and other work to set up the IP and login commands -
Click here to download file for commands list
 Microwave Point-to-Point: FibeAirIP-10
Microwave Point-to-Point: FibeAirIP-10• Manufacturer: Ceragon Networks (Israel)
• Basic parameters:
• Licensed 6-38GHz band (given a choice ODU)
• Bandwidth 7 -56 MHz full duplex (SW tunable)
 • Capacity 10-500Mbps (same HW, license increments)
• Capacity 10-500Mbps (same HW, license increments)• Interface:
• 1x 1000BaseX (SFP)
• 1x 10/100/1000BaseT
• 5x 10/100 BaseT
• 16x E1
• Integrated Ethernet switch
FibeAirIP-10: The main advantages
• Native TDM (E1) anativníEthernet, with no kind of traffic is mapped over the other, both dynamically share a common bandwidth
• Maximálnívyužití bandwidth
• Low transport delay (<200us 400mbps="" gbe="" nbsp="" p="">• Unique 8-state adaptive modulation for maximum availability, seamless and flawless switching
• Extended support QoS (IPv4/IPv6, Q-in-Q, STP / RSTP / MSTP, ...)
• Statistics (radio, transmission, operation)
• SNMP and HTTP management
• Scalable solution for optimal distribution points (6U)
• CertifikovánoMEF MEF-9-14 (for EPL, EVPL, E-LAN)
• Compact IDU (1U), compact ODU (2.5 kg), low power consumption
• Full scalability (1 +1, 2 +0, Hot standby ...)
  |
| Add caption |
• Connect a serial cable to the terminal port
• Setting up HyperTerminal:
• Bit rate: 115200, data bits: 8, parity: none, stop bits: 1 Flow Control: no
• Recommended: type VT-100, size: 24 rows, 80 columns
• Default login:
 • User: admin
• User: admin• Password: admin
• After pressing
• The IP address IDU:
• IP-10 :/> cdmanagement / networking / ip-address
• IP-10 management :/ / networking / ip-address> get ip-address
Basic Commands
The following basic commands are available when you first log in, if you belong to the Operator user
group:
ls List entities
get Get parameter
set Set parameter
help Help
cd Change directory
exit Exit CLI
logout Logout from CLI
cli-ver CLI version
cls Clear screen
shell Enter secondary shell
write Write the current switch configuration to the configuration file
show-tree Show entity tree
find Search for a string in the parameter's entity name and information fields
lsp List entity parameters and commands
echo echoing free text to the console
Note: To perform the operations in this guide, you should log in as follows:
User: admin or operator
Password: admin
Basic System Configuration
Setting IP Addresses
To define a new IP address, do the following at the main unit:
1. Log in as follows:
User: admin or operator
Password: admin
2. At the command prompt, type: cd management/networking/ip-address/, and press Enter.
3. Type: get ip-address, and press Enter. This will give you the current IP address.
4. Type: set ip-address
Adding Users
To define a new user, do the following:
1. Log in.
2. At the command prompt, type: cd management/mng-services/users/, and press Enter.
3. Type: add-user , and press Enter.
4. Type the password for the new user.
Navigating between Stacked Units
Going from the Main Unit to a Different Unit
After log-in, a prompt always appears at the main unit. Tto change the prompt to a different unit, do the
following:
1. Log in.
2. At the command prompt, type: cd /platform/shelf-manager/, and press Enter.
3. Type: logon-unit , and press Enter.
The prompt will change according to the relevant slot ID. For example, the prompt for a unit located in slot
3 will show:
IP-10-SLOT-3:/>
Returning to the Main Unit
In order to go back to the main unit, do the following:
1. Log in.
2. At the command prompt, type: cd /platform/shelf-manager/, and press Enter.
TDM Trail Management
Defining a TDM Trail
To define a TDM trail, do the following at the main unit:
1. Log in.
2. At the command prompt, type: cd /interfaces/pdh/trails/, and press Enter.
3. Type: add-trail
2 slot #> , and press Enter.
Argument Description:
• Trail-ID: up to 16 alphanumeric characters
• Trail description: string of up to 32 characters
• ACM priority: high or low
• Operational/reserved: reserved trails are introduced in the database and the bandwidth won’t be
used for TDM traffic (it may be used for ethernet traffic) but traffic does not flow. For operational
trails, bandwidth is fully allocated and traffic flows.
• Protected/unprotected: unprotected trails map between two interfaces only. Protected trails map
between an end-point interfaces and two other interfaces, the first of which is the primary path and
the second of which is the secondary path (see the SNCP section below).
• Interface slot: slot number of the IDU containing the interface (from 1 to 6).
• Interface type: line (E1/T1) or radio
• Interface number: the number of the E1/T1 interface or radio VC to be used.
o For E1/T1 it can be 1 to 32 (1 to 16 if no extra 16 E1 T-card is installed)
o For radio, the maximum number depends on the radio script being used
Unprotected trail example:
add-trail id1 desc1 high operational unprotected 1 line 1 1 radio 1.
No comments:
Post a Comment